Osteopathic practice
Harry Fischer Osteopath, M.Sc. DPO HP
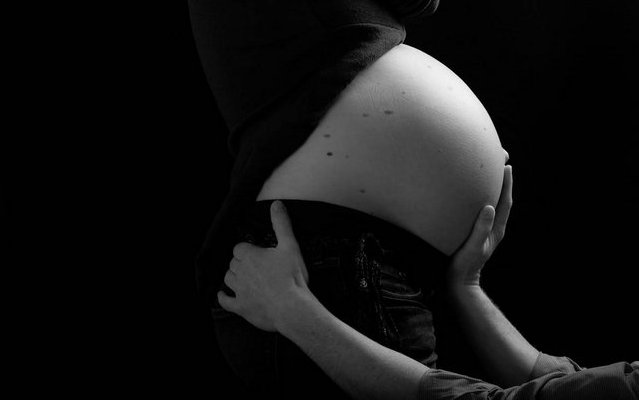




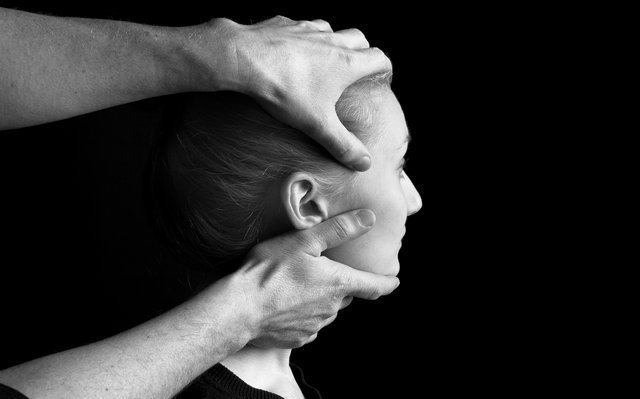



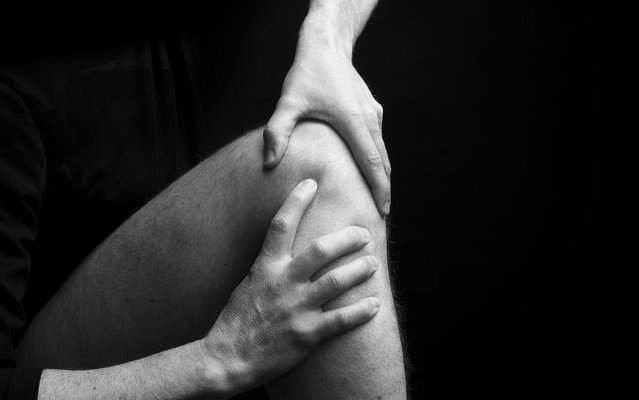



Fields of application for Osteopathy
Basically Osteopathy can be applied to all malfunctions of the body, regardless of how long they have existed:
♦ e.g. with tensions and injuries
♦ complaints of muscles and ligaments
♦ tennis elbow
♦ herniated discs
♦ consequences of accidental injuries
♦ TMJ problems / craniomandibular malfunction
♦ stomach and digestive problems
♦ dyspeptic symptoms
♦ headache
♦ tinnitus
♦ dizziness
♦ incontinence
♦ premenstrual discomfort
♦ and further discomforts
Basically Osteopathy can be applied to all malfunctions of the body, regardless of how long they have existed:
♦ e.g. with tensions and injuries
♦ complaints of muscles and ligaments
♦ tennis elbow
♦ herniated discs
♦ consequences of accidental injuries
♦ TMJ problems / craniomandibular malfunction
♦ stomach and digestive problems
♦ dyspeptic symptoms
♦ headache
♦ tinnitus
♦ dizziness
♦ incontinence
♦ premenstrual discomfort
♦ and further discomforts
Osteopathy for expectant and new mothers
During pregnancy, birth, lactation and involution phase, the body and the mind adapt to the baby's needs in a very short time.
In the complaints mentioned below osteopathy can support and help:
♦ heartburn in pregnancy
♦ back pain in pregnancy
♦ breastfeeding problems
♦ birth scars
♦ fatigue
♦ subsidence and bladder complaints
During pregnancy, birth, lactation and involution phase, the body and the mind adapt to the baby's needs in a very short time.
In the complaints mentioned below osteopathy can support and help:
♦ heartburn in pregnancy
♦ back pain in pregnancy
♦ breastfeeding problems
♦ birth scars
♦ fatigue
♦ subsidence and bladder complaints
Osteopathy for babies / children
During pregnancy and especially the stage of labor, the body has to adapt to the processes. Through various factors (like complicated birth situation, stuck in the pelvis during childbirth, medication during pregnancy / birth, use of forceps or ventouse) the adaptation processes are limited. This can cause physical function, developmental, learning or concentration problems.
Osteopathy cannot eliminate the cause of such disorders but can often successfully treat the consequences of a birth trauma or an early childhood trauma.
Osteopathy for babies and children handles the following clinical pictures and their consequences:
♦ cry-children (cry-babies), reject children
♦ torticollis, body asymmetry and the so-called KISS syndrome
♦ craniofacial deformities
♦ indigestion, colic
♦ overstretch and preferential attitude
♦ restlessness and lack of concentration
♦ developmental delays
♦ allergies and colds inclination
♦ malocclusions and teeth-gnashing
♦ infections of the middle ear and sinus and further discomforts
During pregnancy and especially the stage of labor, the body has to adapt to the processes. Through various factors (like complicated birth situation, stuck in the pelvis during childbirth, medication during pregnancy / birth, use of forceps or ventouse) the adaptation processes are limited. This can cause physical function, developmental, learning or concentration problems.
Osteopathy cannot eliminate the cause of such disorders but can often successfully treat the consequences of a birth trauma or an early childhood trauma.
Osteopathy for babies and children handles the following clinical pictures and their consequences:
♦ cry-children (cry-babies), reject children
♦ torticollis, body asymmetry and the so-called KISS syndrome
♦ craniofacial deformities
♦ indigestion, colic
♦ overstretch and preferential attitude
♦ restlessness and lack of concentration
♦ developmental delays
♦ allergies and colds inclination
♦ malocclusions and teeth-gnashing
♦ infections of the middle ear and sinus and further discomforts
Definition of Osteopathy and its techniques
Osteopathic medicine serves mainly to recognize and treat the functional disorders. The osteopaths make the diagnosis by using specific techniques that are performed with their hands. The osteopaths distinguish three major systems of the human body and, accordingly, three main areas of Osteopathy:
Parietal Osteopathy
treatment of the musculoskeletal system and the peripheral nervous system.
Visceral Osteopathy
treatment of internal organs and the enteric nervous system.
Cranial Osteopathy
treatment of the skull and the central nervous system in connection with
the Dural tube of the spinal canal and the sacrum.
The application of one of the numerous osteopathic techniques is often done already during the investigation. Here is a selection:
Osteopathic medicine serves mainly to recognize and treat the functional disorders. The osteopaths make the diagnosis by using specific techniques that are performed with their hands. The osteopaths distinguish three major systems of the human body and, accordingly, three main areas of Osteopathy:
Parietal Osteopathy
treatment of the musculoskeletal system and the peripheral nervous system.
Visceral Osteopathy
treatment of internal organs and the enteric nervous system.
Cranial Osteopathy
treatment of the skull and the central nervous system in connection with
the Dural tube of the spinal canal and the sacrum.
The application of one of the numerous osteopathic techniques is often done already during the investigation. Here is a selection:
| ♦ | Strain- / Counterstrain- or Positional- release techniques: short specific stimuli cause "Reactions" in the treated tissues |
| ♦ | Muscle- energy- techniques: various MET techniques improve the tone and blood circulation in the muscles. |
| ♦ | High-Velocity Low-amplitude techniques (HVLA): small, fast applications change the position of a structure. |
| ♦ | Fascial release techniques: stimulate the fascia on to unwind itself (unwinding). |
| ♦ | Visceral techniques: improve the general sliding movements of the internal organs. |
| ♦ | Cranial techniques: eliminate blockages in the cranial system and harmonize the primary rhythm |
| ♦ | see further techniques in the specialized literature. |
Discovery of Osteopathy
In 1864 the American country physician A.T. Still had to experience how three of his children died of meningitis.
He then started to search for a "better" medicine that had to be both simple and successful. He quickly recognized the enormous potential of the hands and based on the methods of the "bonesetters" developed refined techniques which became the basis of all modern manual medicine. He understood the human being as a unity of body, mind and soul “always as part of a perfect creation.”
Still was convinced that the ability of the body to heal itself depends on the flow of body fluids (blood, lymph and "nervous water") and that the flow so essential for health can be hindered by anatomical disturbances - called lesions by him. He warns his colleagues: "The duty of the practitioner is not to heal the sick, but to adjust a part of the whole system, so that the streams of life can keep flowing and can irrigate the dry fields. The rest is done by nature.”
Still was not interested in the heroic treatment of "pathologies"; using his manual techniques he simply wanted to provide nature the optimum setting for its mighty work.
In his words: “To find health is the mission of the doctor – anyone can find disease.”
Since only nature has the ability to cure itself Still never understood himself as a "healer", but as a humble craftsman with boundless confidence in nature.
Through his huge treatment successes Still had to find a name for his medical philosophy. Working with manual techniques on the bone (Greek osteon-) and easing indirectly the sufferings (Greek -patheios)of his patients, he blended two Greek roots and invented the name OSTEOPATHIE.
When Still died in 1917, there were over 20,000 osteopaths all over the world practicing his "better" medicine.
In 1864 the American country physician A.T. Still had to experience how three of his children died of meningitis.
He then started to search for a "better" medicine that had to be both simple and successful. He quickly recognized the enormous potential of the hands and based on the methods of the "bonesetters" developed refined techniques which became the basis of all modern manual medicine. He understood the human being as a unity of body, mind and soul “always as part of a perfect creation.”
Still was convinced that the ability of the body to heal itself depends on the flow of body fluids (blood, lymph and "nervous water") and that the flow so essential for health can be hindered by anatomical disturbances - called lesions by him. He warns his colleagues: "The duty of the practitioner is not to heal the sick, but to adjust a part of the whole system, so that the streams of life can keep flowing and can irrigate the dry fields. The rest is done by nature.”
Still was not interested in the heroic treatment of "pathologies"; using his manual techniques he simply wanted to provide nature the optimum setting for its mighty work.
In his words: “To find health is the mission of the doctor – anyone can find disease.”
Since only nature has the ability to cure itself Still never understood himself as a "healer", but as a humble craftsman with boundless confidence in nature.
Through his huge treatment successes Still had to find a name for his medical philosophy. Working with manual techniques on the bone (Greek osteon-) and easing indirectly the sufferings (Greek -patheios)of his patients, he blended two Greek roots and invented the name OSTEOPATHIE.
When Still died in 1917, there were over 20,000 osteopaths all over the world practicing his "better" medicine.
Education
A reputable osteopathic training lasts at least five years.
To complete a specialized training for children takes again at least two years.
Almost all students have made before therapeutic experience as a physical therapist, medical practitioner or physician.
In the training there are taught basic medical subjects such as anatomy and physiology exclusively under their functional aspects with regard to the human being as an individual unit.
At the same time the hand is perfected as a medical instrument.
Although there are no fixed principles in osteopathy, most osteopaths act on basis of the following principles:
A) Function and structure influence each other continuously.
B) Every person forms an inseparable and unique unity of body, mind and soul,
which means more than the sum of its parts.
C) The natural power of self-organization is solely responsible for the healing.
The osteopath tries only to create the optimum conditions for these natural healing processes.
A reputable osteopathic training lasts at least five years.
To complete a specialized training for children takes again at least two years.
Almost all students have made before therapeutic experience as a physical therapist, medical practitioner or physician.
In the training there are taught basic medical subjects such as anatomy and physiology exclusively under their functional aspects with regard to the human being as an individual unit.
At the same time the hand is perfected as a medical instrument.
Although there are no fixed principles in osteopathy, most osteopaths act on basis of the following principles:
A) Function and structure influence each other continuously.
B) Every person forms an inseparable and unique unity of body, mind and soul,
which means more than the sum of its parts.
C) The natural power of self-organization is solely responsible for the healing.
The osteopath tries only to create the optimum conditions for these natural healing processes.
Limits of Osteopathy
Osteopathy reaches its limits, when the self-healing powers of the body are not sufficient.
Osteopathy is not an emergency medicine, it cannot save life in the case of a heart attack or a stroke.
Open wounds, fractures, burns or other injuries must always be treated first by a physician.
Similarly mental disorders such as Depression cannot be treated by the hands of an osteopath.
Osteopathy reaches its limits, when the self-healing powers of the body are not sufficient.
Osteopathy is not an emergency medicine, it cannot save life in the case of a heart attack or a stroke.
Open wounds, fractures, burns or other injuries must always be treated first by a physician.
Similarly mental disorders such as Depression cannot be treated by the hands of an osteopath.
Questionnaire
Questionnaire infants
Questionnaire children/ boys and girls
Questionnaire adults (female)
Questionnaire adults (male) Information
Costs Links
Baby subjects
♦ www.bambiona.de/thema/baby
Osteopathie
♦ www.r-o-d.info
♦ www.bao-osteopathie.de
Sports
♦ Running running style woman: Tirunesh Dibaba Video
♦ Running running style man: Haile Gebrselassie Video 1 Video 2
♦ Running ABC: Video 1 Video 2
♦ One-shot jumps simply: Video
♦ Sophisticated variant: Video
♦ Lower back exercises: Video
♦ Abdominal exercises: Video
Harry Fischer
born 1969 Sportsman - Triathlon 1988-1994
Osteopath
All possible treatments for osteopathy,
no age restriction for treatment
Focuses:
Temporomandibular joint; mandibula malformation;
bite malformation (oclusion defects); babies;
young children; teens
Summary of the education:
♦ B Power - and Fitness trainer at bavarian Power and
Weightlifting Federation (BGKV)
♦ continuing education at ACON osteopathy; chriopractice and neural therapy
♦ 5 years of osteopatic education at IFAO
with a degree based of the criteria of BAO
♦ BAO University of Wales, Master Course for children osteopatie - 4 years;
and from 2011 till 2014 - research projects
♦ 2014 continuing education for Sonography "Locomotor System" according to the guidelines
of DEGUM (German Association for medical ultrasound e.V.)
Sportsman - Triathlon 1988-1994
Osteopath
All possible treatments for osteopathy,
no age restriction for treatment
Focuses:
Temporomandibular joint; mandibula malformation;
bite malformation (oclusion defects); babies;
young children; teens
Summary of the education:
♦ B Power - and Fitness trainer at bavarian Power and
Weightlifting Federation (BGKV)
♦ continuing education at ACON osteopathy; chriopractice and neural therapy
♦ 5 years of osteopatic education at IFAO
with a degree based of the criteria of BAO
♦ BAO University of Wales, Master Course for children osteopatie - 4 years;
and from 2011 till 2014 - research projects
♦ 2014 continuing education for Sonography "Locomotor System" according to the guidelines
of DEGUM (German Association for medical ultrasound e.V.)
born 1969
 Sportsman - Triathlon 1988-1994
Osteopath
All possible treatments for osteopathy,
no age restriction for treatment
Focuses:
Temporomandibular joint; mandibula malformation;
bite malformation (oclusion defects); babies;
young children; teens
Summary of the education:
♦ B Power - and Fitness trainer at bavarian Power and
Weightlifting Federation (BGKV)
♦ continuing education at ACON osteopathy; chriopractice and neural therapy
♦ 5 years of osteopatic education at IFAO
with a degree based of the criteria of BAO
♦ BAO University of Wales, Master Course for children osteopatie - 4 years;
and from 2011 till 2014 - research projects
♦ 2014 continuing education for Sonography "Locomotor System" according to the guidelines
of DEGUM (German Association for medical ultrasound e.V.)
Sportsman - Triathlon 1988-1994
Osteopath
All possible treatments for osteopathy,
no age restriction for treatment
Focuses:
Temporomandibular joint; mandibula malformation;
bite malformation (oclusion defects); babies;
young children; teens
Summary of the education:
♦ B Power - and Fitness trainer at bavarian Power and
Weightlifting Federation (BGKV)
♦ continuing education at ACON osteopathy; chriopractice and neural therapy
♦ 5 years of osteopatic education at IFAO
with a degree based of the criteria of BAO
♦ BAO University of Wales, Master Course for children osteopatie - 4 years;
and from 2011 till 2014 - research projects
♦ 2014 continuing education for Sonography "Locomotor System" according to the guidelines
of DEGUM (German Association for medical ultrasound e.V.)
Practice Wuppertal Hagenauer Str. 30, 42107 Wuppertal
Practice Hückeswagen Etapler Platz 2, 42499 Hückeswagen
 |  |  |  |
| Hagenauer Str. 30 42107 Wuppertal | Entrance to the elevator on the 2nd floor |
From the elevator hall to right | Osteopathic practice |
Practice Hückeswagen Etapler Platz 2, 42499 Hückeswagen
Harry Fischer
Practice Wuppertal
Hagenauer Str. 30
42107 Wuppertal
Fon 0202 - 254 16 16
email office@h-fischer.com
Practice Hückeswagen
Etapler Platz 2
42499 Hückeswagen
Fon 0202 - 2541616
email office@h-fischer.com
Practice Wuppertal
Hagenauer Str. 30
42107 Wuppertal
Fon 0202 - 254 16 16
email office@h-fischer.com
Practice Hückeswagen
Etapler Platz 2
42499 Hückeswagen
Fon 0202 - 2541616
email office@h-fischer.com
Name u. Anschrift:
Harry Fischer
Hagenauer Str. 30
42107 Wuppertal
Kontaktdaten:
Telefon: 0202 - 254 16 16
Telefax: 0202 - 3190 8458
Email: harry@h-fischer.com
Webadresse: www.h-fischer.com
Profession:
Medical Practitioners in Germany.
The activity as a medical practitioner is based on the Medical Practitioners Act and the 1st Implementing of the Medical Practitioners Act. The code of professional rules is located in the Professional Order for medical practitioners, the Code of Ethics of the Association of German Medical Practitioners and the schedule of fees for medical practitioners. The fee schedule can be ordered at the Federation.
Heilpraktikererlaubnis Heilpraktiker Urkunde
Authority:
Health Department Wuppertal
Willy-Brandt-Platz 19
42105 Wuppertal
Tel. 0202 - 563-2800
Health Department Oberbergischer Kreis
Am Wiedenhof 1 - 3
51643 Gummersbach
Tel. 02261 - 88 53 11
Professional Regulations:
Heilberufe-Kammergesetz
Professional Association: ROD; www.r-o-d.info
ROD Registereintrag
Responsible for content acc. § 6 MDStV:
Harry Fischer (Adresse wie oben)
DISCLAIMER
Online content
The osteopathic consulting office of H. Fischer accepts no liability for the topicality, correctness, completeness or quality of the information provided. Liability claims against the author relating to material or immaterial nature, caused by the use or disuse of the information or the use of incorrect and incomplete information are excluded, unless there is no evidence of the author’s intentional or grossly negligent blame. All offers are not binding. The author expressly reserves the right to change parts or the entire offer without prior notice, to add, to delete or to stop the publication temporarily or permanently.
Copyright and Trademark Law
The author strives to respect the copyrights of the graphics, sound files, video sequences and texts, to use his own graphics, sound files, video sequences and texts or to use license-free graphics, sound files, video clips and texts. All brands and trademarks offered in the Internet and possibly protected by third parties are subject to the provisions of applicable trademark law and the ownership rights of the copyright owner. The mere mentioning does not mean that trademarks are not protected by law! The copyright for objects made and published by the author himself remains solely with the author. Any reproduction or use of such graphics, audio and video clips and texts in other electronic or printed publications is not permitted without explicit approval of the osteopathic consulting office.
Data protection
So far as there is the possibility to enter personal or business data (email addresses, names, addresses), the disclosure of this data by the user is on a voluntary basis. The use and payment of all services offered - if technically possible and reasonable – is allowed also without disclosing such data or by providing anonymous data or a pseudonym..
Legal validity of this disclaimer
This disclaimer is to be regarded as part of the Internet offer referred to on this page. If sections or particular formulations of this text are not, no longer or not completely correct, the remaining parts of the document remain unaffected in their content and validity.
Harry Fischer
Hagenauer Str. 30
42107 Wuppertal
Kontaktdaten:
Telefon: 0202 - 254 16 16
Telefax: 0202 - 3190 8458
Email: harry@h-fischer.com
Webadresse: www.h-fischer.com
Profession:
Medical Practitioners in Germany.
The activity as a medical practitioner is based on the Medical Practitioners Act and the 1st Implementing of the Medical Practitioners Act. The code of professional rules is located in the Professional Order for medical practitioners, the Code of Ethics of the Association of German Medical Practitioners and the schedule of fees for medical practitioners. The fee schedule can be ordered at the Federation.
Heilpraktikererlaubnis Heilpraktiker Urkunde
Authority:
Health Department Wuppertal
Willy-Brandt-Platz 19
42105 Wuppertal
Tel. 0202 - 563-2800
Health Department Oberbergischer Kreis
Am Wiedenhof 1 - 3
51643 Gummersbach
Tel. 02261 - 88 53 11
Professional Regulations:
Heilberufe-Kammergesetz
Professional Association: ROD; www.r-o-d.info
ROD Registereintrag
Responsible for content acc. § 6 MDStV:
Harry Fischer (Adresse wie oben)
DISCLAIMER
Online content
The osteopathic consulting office of H. Fischer accepts no liability for the topicality, correctness, completeness or quality of the information provided. Liability claims against the author relating to material or immaterial nature, caused by the use or disuse of the information or the use of incorrect and incomplete information are excluded, unless there is no evidence of the author’s intentional or grossly negligent blame. All offers are not binding. The author expressly reserves the right to change parts or the entire offer without prior notice, to add, to delete or to stop the publication temporarily or permanently.
Copyright and Trademark Law
The author strives to respect the copyrights of the graphics, sound files, video sequences and texts, to use his own graphics, sound files, video sequences and texts or to use license-free graphics, sound files, video clips and texts. All brands and trademarks offered in the Internet and possibly protected by third parties are subject to the provisions of applicable trademark law and the ownership rights of the copyright owner. The mere mentioning does not mean that trademarks are not protected by law! The copyright for objects made and published by the author himself remains solely with the author. Any reproduction or use of such graphics, audio and video clips and texts in other electronic or printed publications is not permitted without explicit approval of the osteopathic consulting office.
Data protection
So far as there is the possibility to enter personal or business data (email addresses, names, addresses), the disclosure of this data by the user is on a voluntary basis. The use and payment of all services offered - if technically possible and reasonable – is allowed also without disclosing such data or by providing anonymous data or a pseudonym..
Legal validity of this disclaimer
This disclaimer is to be regarded as part of the Internet offer referred to on this page. If sections or particular formulations of this text are not, no longer or not completely correct, the remaining parts of the document remain unaffected in their content and validity.